If cell wall composition influences on the structure and functionality of the tissues, the kidney-shaped gall morphotype on both Baccharis species should present similar immunolabeling for Senegenin pectins and associated proteins. Our objective is to evaluate histochemically and immunocitochemically the presence and distribution of pectins and AGPs during gall development, checking their association with the functional aspects of gall tissue layers. Ergosterol According to this anatomical description, the parenchymatic cells and the secretory ducts hypertrophy as the galls mature. By the time the stimuli for the maintenance of gall tissues stop, the gall naturally opens, and the gall inducer emerges, indicating the existence of transformations in the status of the cell walls, and their components. One of the cell wall components, the pectins, was histochemically detected in all tissue layers of non-galled and galled samples by the positive reaction to ruthenium red and coriphosphine. This second reagent has revealed a slight difference of pectin detection with a weaker fluorescence in the cell walls of the secretory ducts. Ruthenium red has been considered a nonspecific reagent for pectins, or specific for unesterified pectins. The la er author also proposes that ruthenium red stains more intensely the cell walls where deesterification has occurred, i. e., it may stain more intensely low methyl-esterified pectins and less intensely the high methylesterified pectins. The weak staining with ruthenium red in gall samples may be indicative of pectins de-methylesterification during gall maturation and senescence. The histochemical test with coriphosphine was used to confront these results. Coriphosphine does not react with cellulose, but has affinity to esterified pectins. So, the reduced fluorescence observed in the epithelium indicates the presence of low methyl-esterified pectins in the cell walls. Current immunocytochemical analyses labelling of a wide range either of high or low methyl-esterified pectins in non-galled and gall tissues of B. dracunculifolia strongly prove the potential of ruthenium red and coriphosphine for the histochemical detection of overall pectins, but did not corroborate their efficiency for evaluating the degree of pectin esterification. The JIM5 and JIM7 antibodies detected variations on the distribution of pectins in the cell walls of the three plant tissue systems during the development of the kidney-shaped gall of B. dracunculifolia. The variations in the topography and chemical nature of the pectins should be related to the determination of gall shapes, as a network of the domains of the three polysacharides can have the potential to modulate cell wall structure. This modulation was previously tested in the kidney-shaped gall of B. reticularia. Also, the functional aspects of the gall tissue layers, mainly in relation to cell adhesion and expansion, as well 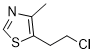 as cell wall porosity, corroborated the assumptions of Knox and McCartney et al.. The degree of methyl-esterification of the homogalacturonans herein analyzed changed from the non-galled tissues towards the senescent galls, which should require the action of pectin methyl esterases or polygalacturonases. Moreover, the de-methyl-esterification can be either randomic or linear, with two distinct biological responses.
as cell wall porosity, corroborated the assumptions of Knox and McCartney et al.. The degree of methyl-esterification of the homogalacturonans herein analyzed changed from the non-galled tissues towards the senescent galls, which should require the action of pectin methyl esterases or polygalacturonases. Moreover, the de-methyl-esterification can be either randomic or linear, with two distinct biological responses.
Month: April 2019
Ventricular hypertrophy in a population free from T2D since gene variants are inherited randomly
We aimed to investigate whether the variant rs5068 within the NPPA locus, previously shown to be associated with ANP levels in plasma, also is associated with incident diabetes. The use of genetic variants should decrease the risk of confounding and reverse causality. Several studies, including our own, have suggested a possible role of natriuretic peptides in etiology of diabetes, however these prospective associations might have been subject to confounding and reverse causality,,. The key finding of this large prospective study is that the carriers of at least one copy of G allele of rs5068, an SNP that was previously shown to be associated with MR-ANP levels in plasma, had lower likelihood of incident diabetes at a follow up of,14 years. Since gene variants are inherited randomly and are not subject to confounding, our data suggest a causal role of the ANP metabolism in diabetes development. The minor allele of rs5068 is associated with higher levels of circulating ANP, as well as with lower BP,. A recent study explored associations between NP system polymorphisms and cardiovascular outcome in a general population with coronary artery disease, demonstrating associations between the rare allele of rs5068 and lower likelihood of hypertension, but also higher circulating NP levels. There is also evidence of association between rs5068 and cardiometabolic protection observed by Cannone and associates, which suggests that this particular single nucleotide polymorphism or genetic loci in linkage disequilibrium might have a protective role via metabolic actions of natriuretic peptides. Cannone and associates managed recently to replicate these findings in a Mediterranean population where carriers of the G allele of rs5068 had lower BP, BMI, and prevalence of hypertension and metabolic syndrome, but found no correlation between rs5068 and T2D after adjusting for BMI. However, since the sample size in this study is relatively small, it warrants replication in larger cohorts. Surprisingly, in our study, the carriers of the minor allele of rs5068 had somewhat higher BMI compared to AA and AG carriers, but we believe that this is due to the small number of minor allele carriers, and this discrepancy was attenuated when using a model where AG+GG alleles were pooled into one variable. Therefore, we do not believe that the actions of rs5068 are mediated by lower BMI. Genetic Rosiridin studies in both animals and humans have established the role of ANP in hypertension, and there is an increasing number of studies suggesting that ANP is involved in glucose metabolism and plays a role in clustering of diabetes and hypertension. The mechanism of Echinacoside action of ANP is not completely understood, but experimental data suggest that low levels of ANP promote future development of insulin resistance and diabetes 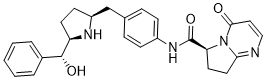 via activation of the renin-angiotensin system which in turn increases oxidative stress and inflammatory response, causes cross-talk between insulin and angiotensin signalling systems, and disturb glucose transporting. ANP infusion has been shown to increase circulating levels of insulin in humans by 50%, and there is evidence of inhibition of glucagon secretion via direct effects on pancreatic b-cells.
via activation of the renin-angiotensin system which in turn increases oxidative stress and inflammatory response, causes cross-talk between insulin and angiotensin signalling systems, and disturb glucose transporting. ANP infusion has been shown to increase circulating levels of insulin in humans by 50%, and there is evidence of inhibition of glucagon secretion via direct effects on pancreatic b-cells.
Implying a lack of sensitization or habituation to handling in a short time frame
Of further interest would be whether this response would subside upon a much longer period of common handling procedures. Pathway analysis demonstrated that handling procedures led to altered expression of immune function related genes with a general decrease in multiple Kaempferide complement system genes as well as a small number of additional immune function related genes. Collectively, these changes likely indicate a minor immune perturbation in the liver following handling procedures. The effects of handling laboratory animals and the resulting alterations in immune response has been documented previously. In general, mild and or acute stressors enhance humoral immune Echinacoside responses while severe or long-term stressors can be immunosuppressive. Stress-related changes in the functional capacity of the immune system have been discussed in a recent review article and include decreased immune cell numbers and functions, decreased response to vaccinations, and increased immunosuppressive pathways and proinflammatory cytokines. Effects of chronic stress on immune function have been well-documented in humans and include effects on both the innate and adaptive immune system. As summarized by Gouin, specific findings include attenuated responses to vaccination, poorer wound healing, exaggerated release of inflammatory mediators, and premature aging of the immune system. Endogenous glucocorticoids are essential for antibody responses and adrenalectomy or anti-glucocorticoid receptor treatment decreases IgM and IgG responses which can be restored by corticosterone replacement. Activation of the complement cascade occurs rapidly and is reported following acute psychological stress in humans with increased circulating levels of C3a, C5a, and Factor Bb. Thus, perturbation of immune system related genes in the liver and a post-handling increase in corticosterone levels at day 2 are consistent with previous reports of acute stress-related effects. Liver gene expression changes were measured in necropsied livers on the day following dose administration and tail vein blood collections. Therefore, the decreased expression of complement genes in light of an increase in other immune genes may reflect a transcriptional feedback loop. In conclusion, the results reported here highlight gene expression changes that occur in laboratory 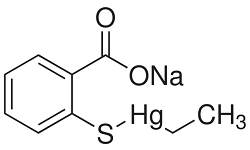 animals during routine handling procedures. These gene expression changes can be viewed as baseline changes upon which additional transcript level alterations resulting from vehicle and/or compound related effects are layered. One can envision the composition of these effects as depicted in Figure 1. This simple additive model illustrates how transcriptional effects at various levels on preclinical animals may add up. If control animals in a study are subjected to the same handling procedures these gene expression changes may be normalized as vehicle related changes are normalized. However, more complex models and interactions with vehicle and/or compound related gene changes cannot be excluded and may warrant further investigation. Synergistic or subtractive interactions with compound mediated effects may confound interpretation of gene changes in a study.
animals during routine handling procedures. These gene expression changes can be viewed as baseline changes upon which additional transcript level alterations resulting from vehicle and/or compound related effects are layered. One can envision the composition of these effects as depicted in Figure 1. This simple additive model illustrates how transcriptional effects at various levels on preclinical animals may add up. If control animals in a study are subjected to the same handling procedures these gene expression changes may be normalized as vehicle related changes are normalized. However, more complex models and interactions with vehicle and/or compound related gene changes cannot be excluded and may warrant further investigation. Synergistic or subtractive interactions with compound mediated effects may confound interpretation of gene changes in a study.
Combines cellulase production and enzymatic hydrolysis into a single biological step and produces sugar aldonates
It has been shown that inhibiting Aurora-A-kinase can result in reexpression of primary cilia. Interestingly, Aurora-A kinase over-expression has been shown to occur in prostate cancer. Another pathway that could be targeted to allow for reexpression of primary cilia is the fatty acid synthesis pathway. Fatty acid synthesis is common in prostate cancer, and blocking this pathway has been shown to cause re-expression of primary cilia in a prostate Gomisin-D cancer cell line. A decrease in primary cilia expression was observed in preinvasive lesions, specifically in a subset of LG and HG PIN. Although LG PIN is not Alisol-A-24-acetate generally thought to be a precursor to invasive prostate cancer, Goeman et al. demonstrate that in a patient with LG PIN in the initial biopsy there was a 30% risk of developing invasive cancer. This was similar to the risk associated with a HG PIN diagnosis. This data suggests that a subset of LG PIN have the potential to develop into invasive prostate cancer. We observed a decrease of primary cilia frequency and length in a subset of LG PIN samples, suggesting that these LG PIN lesions are similar to what is observed in HG PIN. It is possible that these LG PIN lesions with decreased cilia frequency may be precursors to prostate cancer formation. Further work is needed to determine if loss of cilia in LG PIN can be predictive of prostate cancer formation. The frequency of primary cilia in cancers may be indicative of the efficacy of specific Hedgehog-targeted drugs for prostate cancer patients. Numerous Hedgehog-targeted drugs are being investigated both in clinical trials and in laboratories. Since primary cilia are lost in prostate tumors, we hypothesize that prostate cancer patients would not be good candidates for Smo-inhibitor drugs. However, we demonstrate that primary cilia loss does not change in the stroma surrounding cancers. Karlou et al. have shown paracrine Hedgehog signaling in a prostate mouse model, where prostate cancer cells secrete Hedgehog ligand and Smo-dependent Hedgehog AbMole Isovitexin activity is restricted to the prostate tumor stroma. We would predict that Smo-inhibitor drugs would be effective on the prostate cancer stroma, and may hinder the stroma-tumor relationship. However, treating a prostate cancer mouse model with a Smo-inhibitor did not reduce tumor burden, suggesting that Smo-inhibition may not be effective in prostate cancer patients.The conventional biochemical platform featuring enzymatic hydrolysis involves five key steps: pretreatment, cellulase production, enzymatic hydrolysis, fermentation, and product recovery, as shown in Figure 1. Sugars are produced as reactive intermediates for subsequent 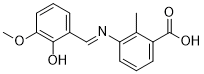 fermentation to fuels and chemicals. The steps involved in overcoming the recalcitrance of cellulosic biomass pretreatment, cellulase production and enzymatic hydrolysis are the three costliest steps in the entire process. Lowering the processing cost of these three steps is essential in order to make cellulosic biorefineries economically viable. One strategy to reduce the processing cost is through process consolidation.
fermentation to fuels and chemicals. The steps involved in overcoming the recalcitrance of cellulosic biomass pretreatment, cellulase production and enzymatic hydrolysis are the three costliest steps in the entire process. Lowering the processing cost of these three steps is essential in order to make cellulosic biorefineries economically viable. One strategy to reduce the processing cost is through process consolidation.
Racial and social factors, including endemic environment could be the underlying explanation
Recipients of organ transplantation are subjected to lifelong immunosuppression. Thus an increased incidence of developing cancer is expected in recipients with longer follow-up. The longer transplant recipients survive, the greater the risk of cancer accumulates. This was supported by the results in our series. We noted, as expected, that the number of  de novo cancers increased as further Procyanidin-B2 follow-up accrued. Moreover, though receiving aggressive treatments after diagnosis, poor survival of those patients with de novo cancers was noted in our series. All the patients who died after the diagnosis had a direct relationship with the de novo cancers. Indeed, the causes of patient later death after LTx are multifactorial including chronic rejection, primary disease recurrence and others. Recent studies have currently considered de novo cancer as the second leading cause of death following cardiovascular complications. It has been clear that tumor recurrence is the major cause of death after LTx for recipients of malignant liver disease. However, after excluding the patients who died of tumor recurrence, our single center study showed that the survival of patients with de novo cancers was significantly lower than those without de novo cancers, suggesting that compared with nontumor factors de novo cancer has contributed more to the later mortality after LTx in Chinese population. Although the incidence and mortality rates in developed countries have been decreasing during the past 25 years, both rates have been increasing in many developing countries. In China, breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer and is ranked the sixth leading cause of death in Chinese women. Except for ill-fitted environmental exposures, lifestyle and behavioral factors, many studies have also suggested that genetic factors are usually associated with the risk of breast cancer. In recent years, the use of genome-wide association studies to screen disease-associated genetic variants, has led to the successful identification of Praeruptorin-B numerous breast cancer susceptibility regions, supporting a polygenic model of breast cancer susceptibility. However, such loci explain only a small percentage of the total risk, and important regions harboring genetic variants associated with breast cancer risk still remain to be identified. It is well accepted that biofilm formation in aquatic ecosystems both enhances survival and persistence of V. cholerae, by providing nutrients and protection from protozoan grazing and phage predation, and that it plays a critical role in the transmission of the pathogen. V. cholerae also forms biofilms while inside infected individuals. Stool samples from cholera patients contain V. cholerae both in biofilm-like clumps and in a planktonic form. The average infectivity of biofilm-like clumps is higher than that of planktonic cells, and growth in biofilm induces a hyper-infectious phenotype, suggesting that V. cholerae biofilms are important in the disease process. Biofilm formation depends on production of a biofilm matrix i.e., exopolysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. In many bacteria exopolysaccharides represent a major portion of the biofilm matrix; and mutants unable to produce exopolysaccharides are impaired in biofilm formation. We have previously isolated VPS, performed initial glycosyl composition and linkage analyses, and identified the gene clusters required for VPS biosynthesis. However, chemical structure of VPS has remained elusive due to difficulties in obtaining its NMR spectra. In this study, we report the chemical structure of VPS, and describe a reliable method for the isolation of VPS from the extracellular material produced by V. cholerae.
de novo cancers increased as further Procyanidin-B2 follow-up accrued. Moreover, though receiving aggressive treatments after diagnosis, poor survival of those patients with de novo cancers was noted in our series. All the patients who died after the diagnosis had a direct relationship with the de novo cancers. Indeed, the causes of patient later death after LTx are multifactorial including chronic rejection, primary disease recurrence and others. Recent studies have currently considered de novo cancer as the second leading cause of death following cardiovascular complications. It has been clear that tumor recurrence is the major cause of death after LTx for recipients of malignant liver disease. However, after excluding the patients who died of tumor recurrence, our single center study showed that the survival of patients with de novo cancers was significantly lower than those without de novo cancers, suggesting that compared with nontumor factors de novo cancer has contributed more to the later mortality after LTx in Chinese population. Although the incidence and mortality rates in developed countries have been decreasing during the past 25 years, both rates have been increasing in many developing countries. In China, breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer and is ranked the sixth leading cause of death in Chinese women. Except for ill-fitted environmental exposures, lifestyle and behavioral factors, many studies have also suggested that genetic factors are usually associated with the risk of breast cancer. In recent years, the use of genome-wide association studies to screen disease-associated genetic variants, has led to the successful identification of Praeruptorin-B numerous breast cancer susceptibility regions, supporting a polygenic model of breast cancer susceptibility. However, such loci explain only a small percentage of the total risk, and important regions harboring genetic variants associated with breast cancer risk still remain to be identified. It is well accepted that biofilm formation in aquatic ecosystems both enhances survival and persistence of V. cholerae, by providing nutrients and protection from protozoan grazing and phage predation, and that it plays a critical role in the transmission of the pathogen. V. cholerae also forms biofilms while inside infected individuals. Stool samples from cholera patients contain V. cholerae both in biofilm-like clumps and in a planktonic form. The average infectivity of biofilm-like clumps is higher than that of planktonic cells, and growth in biofilm induces a hyper-infectious phenotype, suggesting that V. cholerae biofilms are important in the disease process. Biofilm formation depends on production of a biofilm matrix i.e., exopolysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids. In many bacteria exopolysaccharides represent a major portion of the biofilm matrix; and mutants unable to produce exopolysaccharides are impaired in biofilm formation. We have previously isolated VPS, performed initial glycosyl composition and linkage analyses, and identified the gene clusters required for VPS biosynthesis. However, chemical structure of VPS has remained elusive due to difficulties in obtaining its NMR spectra. In this study, we report the chemical structure of VPS, and describe a reliable method for the isolation of VPS from the extracellular material produced by V. cholerae.