TNF-��, an important inflammatory factor, is inhibited indirectly by miRNA-146a, which targets TRAF6 and IRAK1, and directly by miRNA-125b, which targets the 3’UTR of TNF-�� mRNA. More than 700 miRNAs have been identified in mammals to date. These miRNAs are associated with diverse biological processes, such as the regulation of insulin secretion, viral infection, and tumorigenesis. Previous studies have indicated that most miRNAs play a role in innate immune responses and inflammation. In response to inflammation, some miRNAs are up-regulated, while some others are down-regulated. For example, the expression of miRNA-146a, miRNA-155and miRNA-21 are up-regulated in monocytes challenged by LPS, whereas that of AbMole (R)-(-)-Modafinic acid miRNA-125b is down-regulated. miRNA-155 was initially discovered as a proto-oncogene in lymphoma. The overexpression of miRNA-155 has been detected in B-cell lymphomas and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It is also overexpressed in various solid tumors, including lung, breast, pancreatic, and thyroid cancers. The roles of miRNA-155 in various physiological and pathological processes, such as hematopoietic lineage differentiation, inflammation and immunity, have been identified recently. miRNA-155 is required for the development of T cells, B cells, and dendritic cells. Previous studies have shown that miRNA-155 plays an important role in immunoglobulin class switching to IgG in B cells via the targeted repression of the transcription factor PU.1 and activation-induced cytidine deaminase. Other validated target genes of miRNA-155, such as interleukin-1, IkappaB kinase ��, Ets-1, and Meis1, are associated with the hematopoietic and immune systems. miRNA-155 gene knockout mice displayed severe immune response deficiencies after pathogen exposure. In antigen-speci?c in?ammatory responses against autologous tissue, miRNA-155 has been shown to promote autoimmune inflammation. Furthermore, miRNA-155 has been found to be up-regulated in macrophages following stimulation by a broad range of inflammatory mediators. LPS induces the expression of miRNA-155 in the spleens of mice, but this increase in 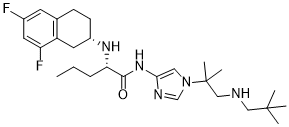 expression is not observed in other organs. The LPS-induced expression of miRNA-155 should be investigated in the liver because this organ is commonly damaged in mice with sepsis. Dexamethasone, a potent synthetic member of the glucocorticoid family, has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, AbMole Trihexyphenidyl HCl antishock, and anti-endotoxin effects. DXM has been widely used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including severe sepsis, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and systemic lupus erythematosus. In the cytoplasm, DXM interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and forms a ligandreceptor complex, which subsequently translocates to the nucleus.
expression is not observed in other organs. The LPS-induced expression of miRNA-155 should be investigated in the liver because this organ is commonly damaged in mice with sepsis. Dexamethasone, a potent synthetic member of the glucocorticoid family, has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, AbMole Trihexyphenidyl HCl antishock, and anti-endotoxin effects. DXM has been widely used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including severe sepsis, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and systemic lupus erythematosus. In the cytoplasm, DXM interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and forms a ligandreceptor complex, which subsequently translocates to the nucleus.